A planet (from Greek πλανήτης αστήρ "wandering star") is a celestial body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals.[a][1][2]
The term planet is ancient, with ties to history, science, mythology, and religion. The planets were originally seen by many early cultures as divine, or as emissaries of the gods. As scientific knowledge advanced, human perception of the planets changed, incorporating a number of disparate objects. In 2006, the International Astronomical Union officially adopted a resolution defining planets within the Solar System. This definition has been both praised and criticized, and remains disputed by some scientists.
The planets were thought by Ptolemy to orbit the Earth in deferent and epicycle motions. Though the idea that the planets orbited the Sun had been suggested many times, it was not until the 17th century that this view was supported by evidence from the first telescopic astronomical observations, performed by Galileo Galilei. By careful analysis of the observation data, Johannes Kepler found the planets' orbits to be not circular, but elliptical. As observational tools improved, astronomers saw that, like Earth, the planets rotated around tilted axes, and some shared such features as ice-caps and seasons. Since the dawn of the Space Age, close observation by probes has found that Earth and the other planets share characteristics such as volcanism, hurricanes, tectonics, and even hydrology.
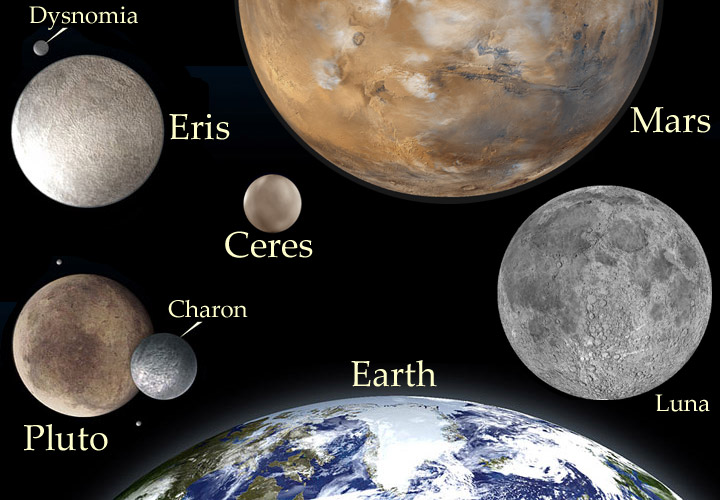
Planets are generally divided into two main types: large, low-density gas giants, and smaller, rocky terrestrials. Under IAU definitions, there are eight planets in the Solar System. In order of increasing distance from the Sun, they are the four terrestrials, Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, then the four gas giants, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Six of the planets are orbited by one or more natural satellites. Additionally, the Solar System also contains at least five dwarf planets[3] and hundreds of thousands of small Solar System bodies.
Since 1992, hundreds of planets around other stars ("extrasolar planets" or "exoplanets") in the Milky Way Galaxy have been discovered. As of December 2010, over 500 known extrasolar planets are listed in the Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia, ranging from the size of terrestrial planets somewhat larger than Earth to gas giants larger than Jupiter.[
See more:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Planet